
Prediabetes
The number of diabetes cases continues to growaround the world. In 1980, 108 million people had diabetes. Today, the disease affects nearly 460 million.
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), the percentage of people with diabetes is 9.3% of all adults. In 2016, diabetes became the world’s seventh leading cause of death.
Yet enormous progress is being made in the prevention of the disease. The detection and subsequent management of prediabetes falls within this framework.
Prediabetes is not a type of diabetes or a disease
Prediabetes is nothing like a disease. Instead, it refers to a phase before the onset of type 2 diabetes.
Diabetes means too much sugar in the blood
Diabetes results in glucoselevels in the blood which are persistently too high; this is called hyperglycaemia. Normally, when sugars from food enter the blood,the pancreas gets to work. The cells of the pancreas secrete insulin, making it possible for our bodies to assimilate glucose and thereby lower blood sugar levels. If a person has diabetes, this mechanism no longer works. Muscles and organs are not getting enough food from carbohydrates which remain stuck in the blood. The pancreas reacts and produces more insulin but this is in vain. Over time, the pancreas becomes exhausted and provides increasingly less of this essential hormone.
Once established, diabetes cannot be cured, though it can sometimes go into remission. A chronic disease, it requires continuous treatment. This starts with a radical change in lifestyle. Eating a healthy diet, losing weight and exercising significantly reduce complications from type 2 diabetes. If these measures are not enough to reduce blood sugar levels, drug treatment will be mandatory.
Prediabetes, a forewarning of type 2 diabetes?
Prediabetes is the state of health preceding diabetes. The fasting glucose level in the blood is abnormally high at between 1.05 g and 1.26 g per litre of blood. This is called glucose intolerance. However, blood sugar does not reach a level that matches that of diabetes. Therefore, prediabetes is not a disease, but rather a phase during which a prediabetic person can act. If no action is taken, there is a risk of complications over time. If nothing is done, it is estimated that people with prediabetes have an 80% chance of developing type 2 diabetes.
Taking action against prediabetes can prevent or delay type 2 diabetes
A patient testing positive for prediabetes test should not be alarmed. It means they have certain factors that can lead to type 2 diabetes. However, if they make a lifestyle change, then diabetes is more likely not to develop five or 10 years later. The treatment for prediabetes mainly consists of adopting better lifestyle and dietary habits.
Eating better, reducing portion size and taking regular exercise generally prevent the progression to type 2 diabetes. Weight control, through the adoption of a balanceddiet based on unprocessed and fresh foods (therefore without additives) is essential. Stopping smoking is also one of the factors that can help with prediabetes. If you have a proven diagnosis of prediabetes, do not hesitate. Ask your doctor for advice as the doctor alone can give you the appropriate treatment for your condition.

What is diabetes?
Diabetes corresponds to a dysfunction of the mechanism controlling sugar in the blood, i.e. glycaemia.
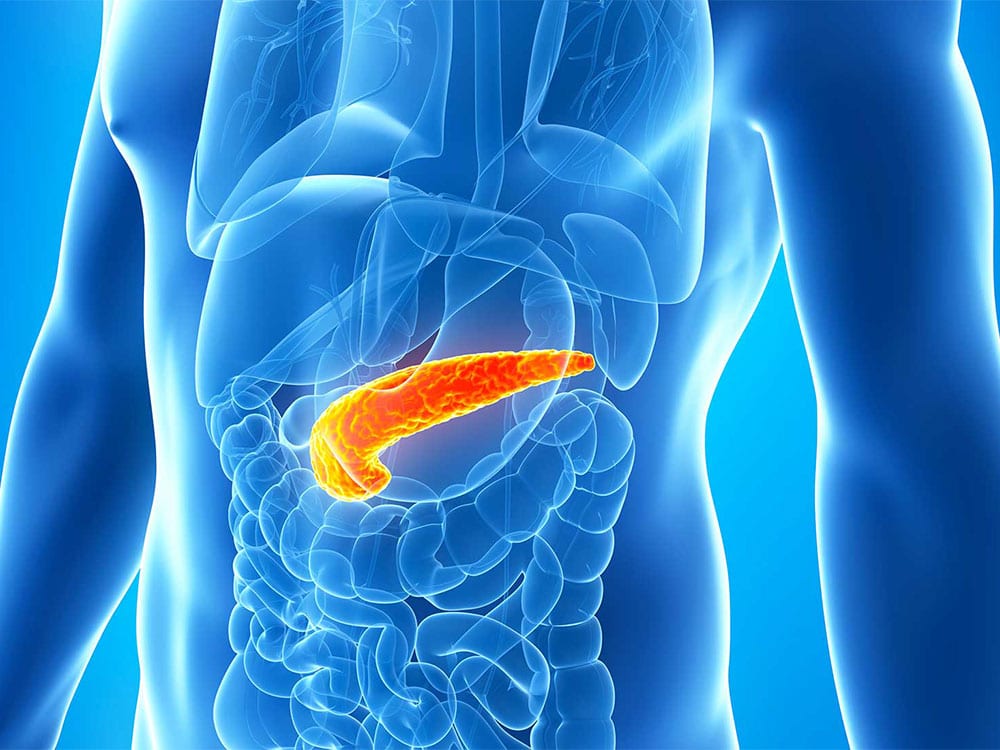
Diabetes summarised in three diagrams
Differentiate diabetes and prediabetes in pictures.

How is diabetes diagnosed?
Diabetes is diagnosed when a fasting blood sugar level greater than or equal to 1.26 g/L is detected and checked twice.

Who is affected and what are the health risks?
Diabetes affects 8.5% of the world’s adult population and is on the rise. It is one of the top 5 causes of death.
Diabetes symptoms
A person with type 2 diabetes may experience the first signs of excess glucose in their blood through various effects.
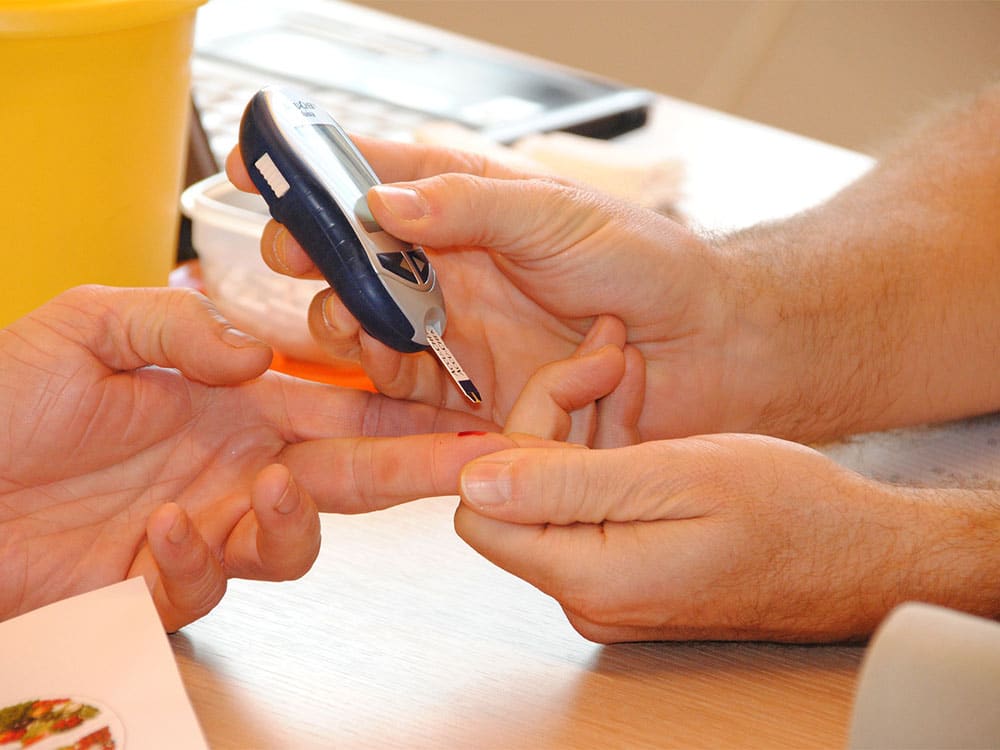

What is the difference between diabetes and prediabetes?
80%* of prediabetics are at risk of developing diabetes within 5-10 years if the situation is left unchecked, because the progression to type 2 diabetesis slow and silent.
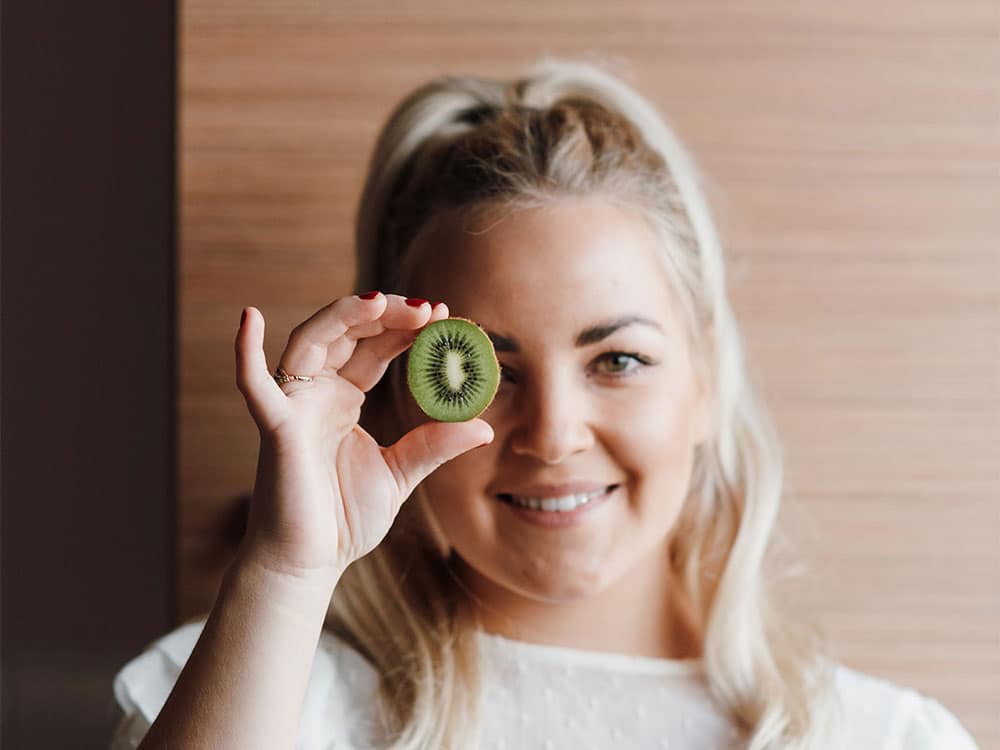

Role of food
Good eating habits and regular physical exercise are the best weapons in the fight against what tends to be called « the disease of the century ».
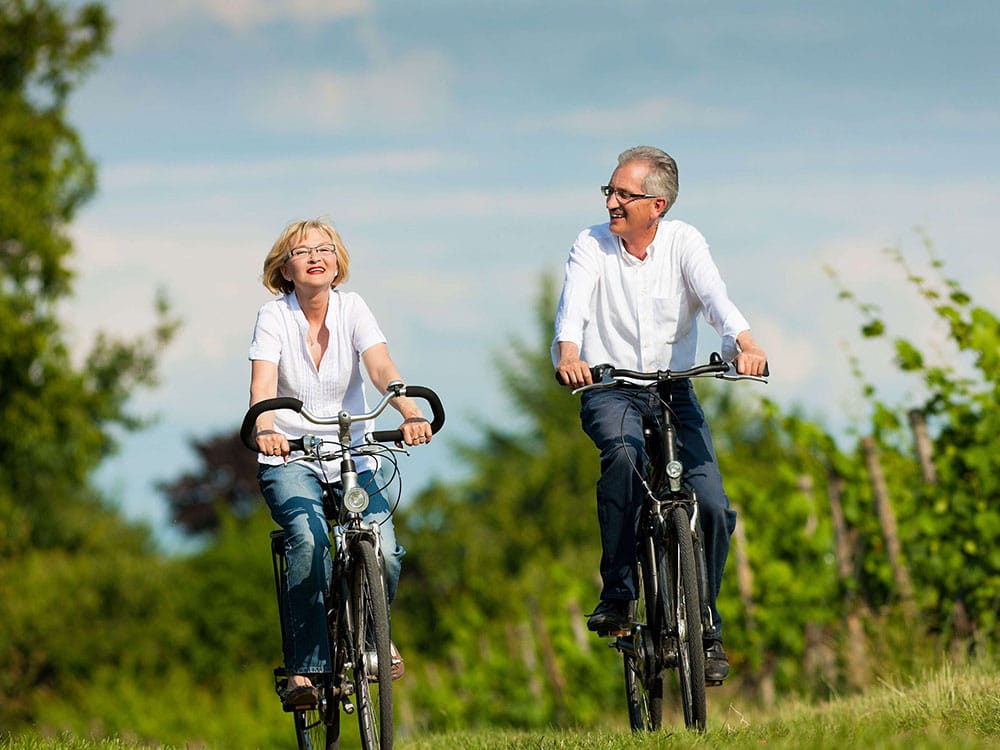

Role of physical activity
Alongside a balanced diet, physical activity is an integral part of the treatment of diabetes.
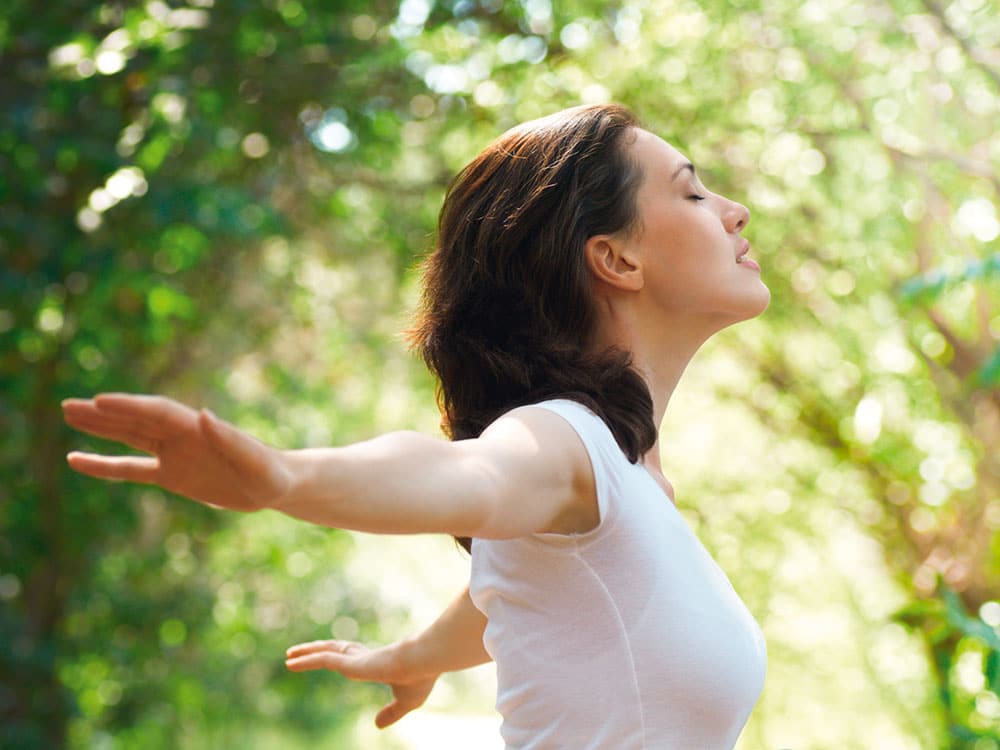

Stress and blood sugar
Lactium® is an ally against chronic stress, sleep problems, eating disorders etc., which are all aggravating factors for the development of diabetes.


Contact information
51 Avenue F. Lobbedez
CS 60946
62033 Arras Cedex
France
Tel : +33 (0)3 21 23 80 00
Fax : +33 (0)3 21 23 80 01
