Useful information
Why do some people suffer from diabetes?
Diabetes is a chronic disease that can be explained by two main factors:
– The body cannot make enough insulin (type 1 diabetes)
– The body fails to use insulin effectively (type 2 diabetes)
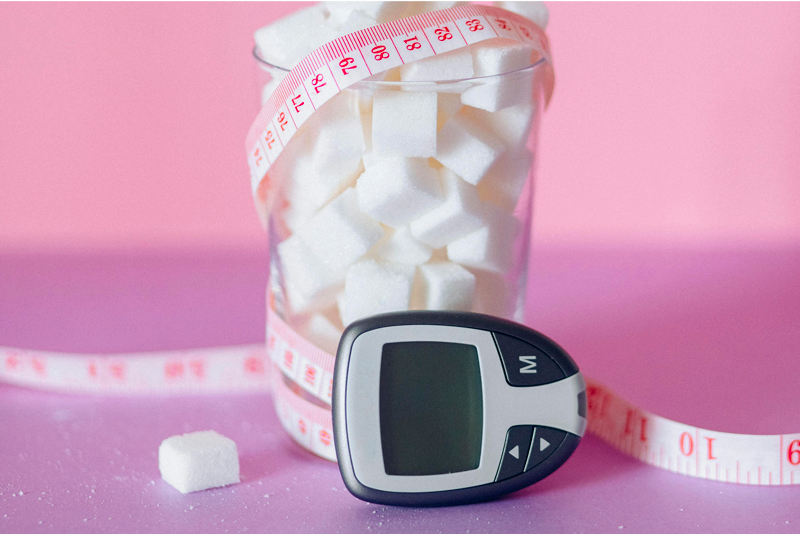
Insulin makes it possible to metabolise sugar to control blood sugar levels. Sugar is essential for health as it provides an important source of energy for muscles, heart, cells and brain.
So, when the body fails to convert sugar into energy, the level of glucose in the blood becomes too high. The main consequence of this is damage to the blood vessels or organs.
Learn more about diabetes
What is the difference between diabetes and prediabetes?
Diabetes is a chronic disease characterised by high levels of sugar in the blood on a permanent basis. It’s a disease that requires proper medical monitoring since it can cause many complications affecting the heart, eyes, kidneys, nerves and even blood vessels.
Prediabetes is characterised by high and abnormal blood sugar levels, but they are not high enough to make people really sick. Prediabetes is diagnosed when the fasting blood sugar level is between 1.10 g/L and 1.25 g/L (a normal fasting blood sugar level is less than 1.10 g/L).
However, 80% of prediabetics are at risk of developing diabetes within five to 10 years if it is left unchecked. In fact, tissues will gradually become resistant to insulin.
It is important to diagnose prediabetes in order to take action and prevent type 2 diabetes. Prediabetes is not a disease, but it can develop into one if left unchecked.
Learn more about the difference between diabetes and prediabetes
What are the symptoms of diabetes?
Diabetes is a disease that should not be taken lightly. It is a chronic disease that can cause serious complications for people suffering from it. The heart, eyes, kidneys, nerves and even blood vessels can be affected by diabetes.
To recognise the disease when it occurs, it is important to understand the symptoms.
The main symptoms of type 2 diabetes are:
– Abnormal thirst and dry mouth
– A need for frequent urination
– Lack of energy and fatigue
– Constant hunger
– Nocturnal incontinence
– Sudden weight loss
– Blurred vision
– Numbness and tingling in the hands and feet
– Slow healing of some wounds and infections
People with type 2 diabetes may also have symptoms related to extreme thirst and hunger, trouble urinating or blurred vision. However, many people with this type of diabetes ignore the disease for a long time because the symptoms are so difficult to spot.
Specific tests (haemoglobin A1C test, fasting plasma glucose test, oral glucose tolerance test, random plasma glucose test etc.) make it possible to establish agenuine diagnosis.
Learn more about diabetes
Am I prediabetic?
Prediabetes can be difficult to diagnose because it does not necessarily cause symptoms and is not yet a disease.
So, while it is not easy to be able to know whether or not you have prediabetes, it is an importantquestion because if nothing is done within five to 10 years, 80% of people with prediabetes will develop type 2 diabetes.
One of the key characteristics of prediabetes are high and abnormal blood sugar levels. However, this level is not high enough to be classed as diabetes. Prediabetes is diagnosed when fasting blood sugar levelsare between 1.10 g/L and 1.25 g/L (normal fasting blood sugar levelsare under 1.10 g/L).
So how do you diagnose prediabetes? Firstly, question your family members. If you have a family history of diabetes, it is important to pay attention to your health.
Several tests can also be performed:
A fasting blood sugar test
A test evaluating the percentage of glycated haemoglobin
A glucose tolerance test
Intermediate values between a healthy status and a diabetic status then make it possible to diagnose prediabetes.
Age, general health, weight and even family history are parameters to take into account when estimating the risk of prediabetes. Do not hesitate to consult your doctor in order to discuss it and take stock of your state of health.
Identify your risks of type 2 diabetes with our Quiz!
How many people have prediabetes?
Prediabetes is not yet a disease, but it does present all the risks of developing into type 2 diabetes. Unfortunately, prediabetes is not an isolated disorder.
In the United States, 96 million people are affected by prediabetes. Out of a population of 328 million in 2019, this represents 30% of Americans. 80% of these 96 million people are likely to become type 2 diabetics. Remember that in this country, medical expenses are much less covered. Prediabetes is therefore not only a health issue, but also an economic one for the world’s most powerful country.
The good news is that prediabetes can be diagnosed early and steps can be taken to prevent the onset of type 2 diabetes.
And what about the rest of the world?
One in 10 people have prediabetes. However, this figure is probably an underestimate because blood sugar tests are not usually employed. However, lifestyles are at risk and blood sugar tests deserve to be rolled out much more extensively. There is a risk is that the number of people with type 2 diabetes will increase over the next few years.
To combat prediabetes and therefore the onset of diabetes, prevention is essential. Indeed, people with prediabetes can still avoid developing diabetes by adopting better lifestyles: balanced diets, regular physical activity and weight loss are all factors that reduce the risk of type 2 diabetes.
Learn more about prediabetes
Can prediabetes be reversed?
Prediabetes is a forerunner to type 2 diabetes and may continue for many years. While it is not yet a disease, it is still notablefor high and abnormal blood sugar levels.
Prediabetes exists when the fasting blood sugar level is between 1.10 g/L and 1.25 g/L. It should be noted that a normal fasting blood sugar level should be under 1.10 g/L. In the prediabetes stage, people are not yet at risk of complications, but they are highly likely to develop type 2 diabetes within five to 10 years if nothing is done to prevent it.
Prediabetes corresponds to the body’s physiological adaptation to an imbalance in blood sugar. Tissues will gradually resist insulin. With the pancreas responsible for filling the sugar gap by producing insulin, the organ gradually becomes exhausted and can no longer perform its function. Type 2 diabetes sets in.
However,unlike diabetes, which is a chronic disease, prediabetes can be reversed. Diagnosed in time, in particular through blood sugar level tests, it is possible to guard against the onset of diabetes.
The right behaviours to adopt to avoid the onset of type 2 diabetes are based on a healthy lifestyle. A balanced diet, regular physical activity as well as possible weight loss make it possible to call time on prediabetes.
Learn more about prediabetes
What are the benefits of food supplements in combatting diabetes?
Diabetes is a chronic disease and as such cannot be reversed. However, it is possible to reduce the risk of complicationsdue to type 2 diabetes by combining drug treatment with an improved lifestyle.
Similarly, these lifestyle choices will reduce the risk of becoming diabetic.
In addition to a healthy diet and regular physical activity, it is also possible to use food supplements that will naturally help manage blood sugar after a meal.
Other food supplements, such as the bioactive from Lactium® Milk, are allies against chronic stress, sleep problems and eating disorders. These disorders are aggravating factors for diabetes.
So, food supplements can help prediabetics to better manage their blood sugar levels and limit the onset of diabetes.
What is the role of food in combatting diabetes?
Diabetes is a chronic disease that most commonly exists in two types: types 1 and 2. Type 2 diabetes accounts for 90% of cases and diet plays a crucial role for people suffering from the disease.
Because diabetes is linked to sugar levels in the blood, a healthy diet is essential to avoid the risks of complications caused by the disease, which can affect the heart, eyes, kidneys and even blood vessels.
Sugar intake must therefore be controlled and saturated fats should also be avoided, which is why people with diabetes are advised to avoid processed food as much as possible.
Certain foods are highly beneficial for people with diabetes. These include pears, avocado, barley, salmon, broccoli and sweet potato. Starchy foods also help keep blood sugar levels stable.
It is also essential to eat three meals a day at regular times and to avoid snacking. It is especially important that people with diabetes should not skip breakfast. Regarding the composition of the meals, they should include:
– Between 10 and 15% protein
– Between 35 and 40% lipids (fats), with an emphasis on unsaturated fats
– Between 50 and 55% carbohydrates (2/3 complex sugars and 1/3 fast-absorbed sugars).
Learn more about the role of food
What role does physical activity play in combatting diabetes?
Sedentary lifestylesare an aggravating factor in type 2 diabetes. While proper monitoring of treatment and a healthy diet are essential, regular physical activity is also strongly recommended.
Numerous studies have shown that regular physical activity contributes to better control of diabetes, in particular glycated haemoglobin levels and insulin resistance. In addition, physical activity helps combat stress and sleep disorders, which are themselves aggravating factors for the disease.
While it is usually advisable to take at least 30 minutes of moderate physical activity, regular shorter sessions of physical activity are preferred for type 2 diabetes patients. Many studies have examined the advantages of dividing up the sessions of physical activity. Indeed, it has been shown that three 10 to 15-minute sessions of intensive exercise are particularly effective in lowering blood sugar and therefore disease control.
Participating in some form of physical activity also makes it possible to lose a little weight and to limit the aggravating risk of being overweight, which is a genuine concern in cases of type 2 diabetes. Nordic walking, jogging, dancing, gymnastics, cycling, swimming: there are lots of sporting activities that can be enjoyed to help people with diabetes to stay in shape.
Learn more about the role of physical activity
Our latest publications
Want to learn more about topics related to blood sugar management?
Here are our most recent blog posts!

Contact information
51 Avenue F. Lobbedez
CS 60946
62033 Arras Cedex
France
Tel : +33 (0)3 21 23 80 00
Fax : +33 (0)3 21 23 80 01
Pep2Dia® is a brand of the Ingredia group